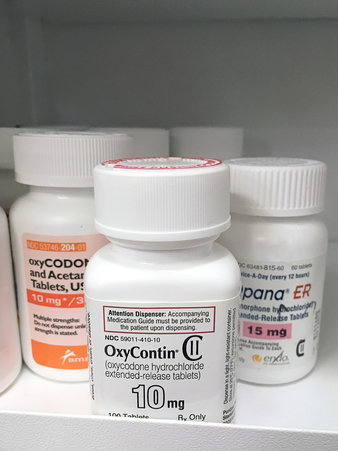
 Opioids, also known as painkillers, reduce the intensity of pain signals reaching the brain and affects those brain areas controlling emotion, which diminishes the effects of a painful stimulus. Some people experience euphoria, since these drugs also impact the reward centers of the brain. Medications in this class include hydrocodone (Vicodin), oxycodone (OxyContin, Percocet), morphine (Kadian, Avinza), codeine, and related drugs. Their use and devastating abuse is making worldwide headlines and has reached epidemic proportions, leading Maryland Governor Hogan to Introduce Legislation to Combat Maryland’s Heroin and Opioid Epidemic.
Opioids, also known as painkillers, reduce the intensity of pain signals reaching the brain and affects those brain areas controlling emotion, which diminishes the effects of a painful stimulus. Some people experience euphoria, since these drugs also impact the reward centers of the brain. Medications in this class include hydrocodone (Vicodin), oxycodone (OxyContin, Percocet), morphine (Kadian, Avinza), codeine, and related drugs. Their use and devastating abuse is making worldwide headlines and has reached epidemic proportions, leading Maryland Governor Hogan to Introduce Legislation to Combat Maryland’s Heroin and Opioid Epidemic.
According to a Senate Caucus on International Narcotics Control report from NIDA, the total number of opioid pain relievers prescribed in the United States has skyrocketed in the past 25 years [1]. The number of prescriptions for opioids has escalated from around 76 million in 1991, to nearly 207 million in 2013, with the United States their biggest consumer globally, accounting for almost 100 percent of the world total for hydrocodone (Vicodin) and 81 percent for oxycodone (Percocet).[2]
Taken as prescribed, opioids can be used to manage pain safely and effectively. However, when they are abused, even a single large dose can cause severe respiratory depression and death. Prescription opioids have a high street market value and, when abused, are often crushed, snorted, and injected. Actors Heath Ledger and Philip Seymour Hoffman, both tragically died from accidental opioid overdose.
Central Nervous System (CNS) Depressants (for anxiety and sleep disorders) or benzodiazepines, include diazepam (Valium), lorazepam (Ativan), alprazolam (Xanax) and often prescribed for anxiety, acute stress and panic attacks. Benzodiazepines are generally not prescribed for long term use because of the risk for developing tolerance (where increasingly larger doses are needed to achieve therapeutic effects), dependence and addiction. Sudden cessation of CNS depressants can be life threatening and withdrawal must be managed by a medical professional.
 Stimulants such as Adderall, Ritalin, and Concerta are commonly prescribed for ADHD and narcolepsy and often illegally bought and sold among high school and college students who use these drugs in a misguided attempt to enhance study. As the name suggests, stimulants increase alertness, attention, and energy, and also elevate blood pressure, heart rate, and respiration.
Stimulants such as Adderall, Ritalin, and Concerta are commonly prescribed for ADHD and narcolepsy and often illegally bought and sold among high school and college students who use these drugs in a misguided attempt to enhance study. As the name suggests, stimulants increase alertness, attention, and energy, and also elevate blood pressure, heart rate, and respiration.
Repeated abuse of some stimulants can lead to feelings of hostility, paranoia, and even psychosis. Repeatedly taking high doses of stimulants may result in a dangerously high body temperature, an irregular heartbeat, and increased risk for cardiovascular failure or seizures.
For other drugs commonly abused, or further information and help, visit the National Institute on Drug Abuse (NIDA).
References:
[1] IMS’s National Prescription Audit (NPA) & Vector One ®: National (VONA).
[2] International Narcotics Control Board Report 2008.. United Nations Pubns. 2009. p. 20